Explain Four Differences Between Normal Fault and Reverse Fault
When an earthquake occurs on one of these faults the rock on one side of the fault slips with respect to the other. They are common at convergent boundaries.

Normal Reverse And Strike Slip Faults Youtube
Lock slides up the incline of the fault plane Thrust faults- compression forces the upthrown block to override the downthrown block at a relatively low angle Strike-slip faults- horizontal displacing adjacent.
. Are their kinematics in any way similar to Normal faulting and Strike SlipIn what way has the knowledge of fault kinematics and dynamics influence the field of Plate Tectonics. Produces steep inclined fault zone REVERSE FAULTS--stress direction and displacementcompression stressespushing togetherupper block slides up the incline of the fault plane in REVERSE OF GRAVITY. Here the hanging wall and the footwall are pushed towards each other causing a compression.
Stike-slip faults are vertical or nearly. The distinction between a reverse fault and a thrust fault is that a reverse fault has a steeper dip greater than 30 degrees. Most faults produce repeated displacements over geologic time.
Normal Faults and Reverse Faults are Dip-Slip Faults - they experience vertical movement in line with the dip of the fault. The main difference between the three faults are. I A normal fault is caused by tensional forces while a reverse fault occurs due to compressional forces.
They are identified by the relative movement of the Hanging Wall and Foot Wall. Reverse faults-Reverse faults are the opposite of normal faults in that two blocks are pushed together instead of away from each other convergent boundary. Block Diagrams Complete the following block diagram exercise in the lab 10 PowerPoint file provided this will be questions 11-14 Part 3.
2 pts Part 2. Faults allow the blocks to move relative to each other. Reverse faults form when the hanging wall moves up.
Start your trial now. How would you explain the differences between thrust fault and Reverse faults. The forces creating reverse faults are compressional pushing the sides together.
This is also a dip slip fault but in thi. First week only 499. If the rock mass on a sloping fault moves downward the it is normally called reverse if the rock above the fault moves upward.
2 pts 10 Explain how to tell the difference between a left-lateral and right-lateral strike-slip fault. An inverse fault in which the fault plane is inclined at an angle equal to or less than 45 is called a pressure fault. A normal fault is a break in the rock caused by pulling away of the rock so that one side slips below the fault line.
In contrast normal fault is caused by tensional stresses which cause the hanging wall and footwall to be pulled apart from each other. The fault surface can be vertical horizontal or at some angle to the. A fault in which Hanging wall HW has apparently come down with respect to the Footwall FW is termed as Normal Fault.
9 Define and explain the difference between a normal fault and a reverse fault. Weve got the study and writing resources you need for your assignments. The dip angle of the sliding surface.
These faults occur where two plates are being compressed and folded upwards due to the colliding pressure. Earthquakes occur on faults - strike-slip earthquakes occur on strike-slip faults normal earthquakes occur on normal faults and thrust earthquakes occur on reverse or thrust faults. Normal faults- pulling apart or extension in the crust very steeply inclined fault zone where one block slides down the fault plane Reverse faults- pushing together where one.
We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Compressional stresses can cause a reverse fault. In a reverse fault the hanging wall moves up relative to the footwall.
In a reverse or thrust fault the hanging wall has moved up relative to the footwall. What is the difference between a normal fault and a reverse fault and under what circumstances would you expect these to form. They are caused by extensional tectonics.
A normal fault appears to be that the suspended wall moves downward relative to the foot wall. Geologic Maps Objectives. A normal fault is a fault where the hanging wall has moved down relative to the footwall.
A strike-slip fault is one along which the movement has been parallel to the fault plane. Iii In a normal faultpart of the fault is exposed to form an escarpment while in a reverse fault the plane is not exposed. A fault is a break in the rocks that make up the earths crust along which on either side rocks move pass eachother.
One block is sliding underneath another or a block is being pushed upwards. How would one distinguish between a normal fault reverse fault and a strike-slip fault. A fault in which hanging wall has apparently gone up with respect to the Footwall is termed as Reverse Fault.
Solution for QUESTION 1 Explain what a fault is and outline the differences between reverse and normal fault. Reverse and thrust faults develop in sectors of the crust that are experiencing compression. NORMAL FAULTS-stress direction and displacement- results from tension pulls apart or extension in the crust.
Faults may range in length from a few millimeters to thousands of kilometers. Together normal and reverse faults are called dip-slip faults because the movement on them occurs along the dip direction -- either down or up respectively. Up to 24 cash back Faults.
A fault is a fracture or zone of fractures between two blocks of rock. Label the types of folds in this diagram and label any of the important features of the folds. This movement may occur rapidly in the form of an earthquake - or may occur slowly in the form of creep.
Larger faults are mostly from action occuring in earths plates. A fault line is the trace of a fault or the line of intersection between the fault line and the earths surface. A reverse fault is a break.
Ii In a normal faultthe up throw move away from down throw while in a reverse fault the up throw moves over down throw. In a Normal Fault the hanging wall moves downwards relative to the foot wall. Section A All all questions in this section.
NORMAL REVERSE THRUST A normal fault is dip slip fault which involves the downward movement of one side of land whereas the other side of the land stays still. Explain why fractures are common in volcanic rocks.
Where And How Do Faults Occur Quora

Fault Types What Are The Three Main Types Of Faults Geology Page
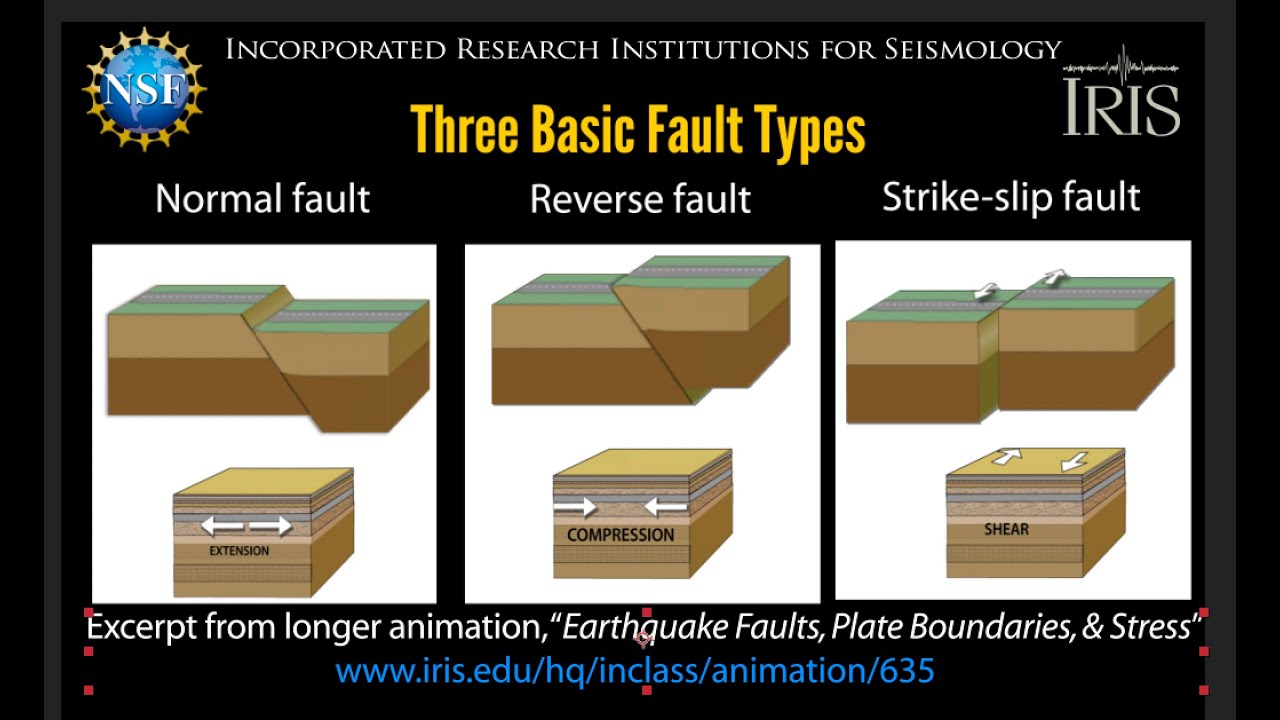
3 Basic Fault Types Normal Reverse Strikeslip Educational 2021 Youtube
What Is A Sense Of Motion And What Type Of Sense Of Motion Does A Thrust Fault Have In Terms Of Earthquake Quora
What Is The Difference Between A Reverse Fault And A Thrust Fault Quora
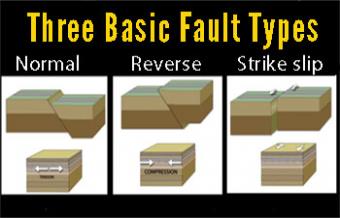
Fault Types 3 Basic Responses To Stress Incorporated Research Institutions For Seismology
How To Recognise A Normal And Reverse Fault Quora
12 3 Fracturing And Faulting Physical Geology

Faults And Folds Reference Tarbuck And Lutgens Pages Ppt Video Online Download

Chapter 9 Earthquakes Ppt Download

Transform Fault Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock

What Is The Difference Between Normal Fault And Reverse Fault Pediaa Com

Fault And Types Of Faults Geology Science
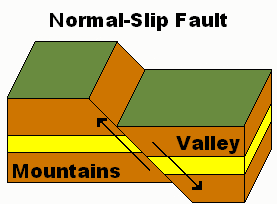
What Is The Difference Between Normal Fault And Reverse Fault Pediaa Com

Types Of Faults In Geology Youtube

What Is A Reverse Fault Definition Locations Example Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Stresses Faults Folds And Earthquakes Ppt Video Online Download


Comments
Post a Comment